Hey there! Did you know that protecting your skin from the sun is just as important for dark skin as it is for fair skin? It's true! Although dark skin has more natural protection against the sun's harmful rays, it's not invincible.
Sun protection is essential because even with dark skin, you can still experience sunburn, skin damage, and even an increased risk of skin cancer. Plus, without proper protection, you could also face the frustrating issue of hyperpigmentation.
So, don't skip the sunscreen, wear protective clothing, and seek shade whenever possible. Your beautiful dark skin deserves the best care and protection under the sun!
Higher Risk of Skin Damage
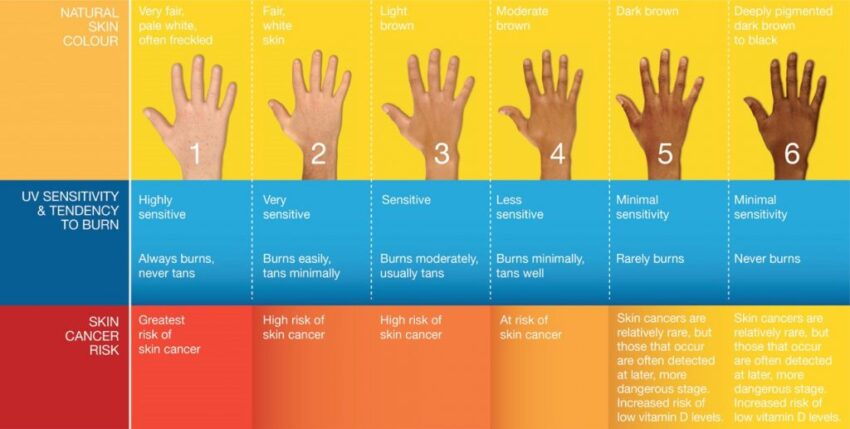
Dark-skinned individuals face a heightened risk of skin damage from sun exposure. Contrary to popular belief, having darker skin doesn't provide complete protection against the harmful effects of UV radiation. While melanin, the pigment responsible for skin color, does offer some natural protection, it isn't enough to prevent premature aging and other skin conditions caused by the sun.
The importance of sunscreen can't be emphasized enough for individuals with dark skin. Sunscreen acts as a barrier, shielding the skin from harmful UV rays. It helps to prevent sunburn, skin cancer, and the development of fine lines and wrinkles. Despite the misconception that dark-skinned individuals don't need sunscreen, it's crucial for them to incorporate it into their daily skincare routine.
Dark skin has a higher concentration of melanin, which provides some inherent protection against the sun. However, this protection isn't sufficient to prevent the long-term damage caused by UV radiation. Therefore, it's essential to choose a broad-spectrum sunscreen with a high SPF, specifically formulated for dark skin. This will ensure adequate protection against both UVA and UVB rays.
Common Misconceptions About Dark Skin and Sun Protection
One common misconception about sun protection and dark skin is that it provides complete immunity against the harmful effects of UV radiation. However, this is far from the truth. Dark skin does have some natural protection against the sun due to higher amounts of melanin, but it isn't enough to provide full protection.
Here are some common myths about dark skin and sun protection that need to be debunked:
- Dark skin doesn't need sunscreen: While dark skin has a natural SPF of around 13.4, it's still important to wear sunscreen. UV radiation can still penetrate dark skin and cause damage, including sunburn, premature aging, and even skin cancer.
- Dark skin doesn't need to reapply sunscreen as often: Sunscreen needs to be reapplied every two hours, regardless of skin color. Sweating, swimming, and rubbing can all remove sunscreen, leaving your skin vulnerable to the sun's harmful rays.
- Dark skin doesn't need a high SPF: Dark skin needs the same level of protection as any other skin tone. Use a broad-spectrum sunscreen with at least SPF 30 to ensure adequate protection.
- Dark skin doesn't need to worry about vitamin D deficiency: While it's true that dark-skinned individuals may have a lower risk of vitamin D deficiency, it's still important to get enough sunlight for vitamin D synthesis. However, it's crucial to balance sun exposure with sun protection to avoid skin damage.
To ensure the best sun protection for dark skin, follow these guidelines and debunk these common myths. Remember, protecting your skin from the sun is essential, regardless of your skin tone.
Sunburn and Sun Damage Can Still Occur
Even with dark skin, you can still experience sunburn and sun damage if you don't take proper sun protection measures. Contrary to popular belief, having dark skin doesn't provide complete immunity to the harmful effects of the sun's ultraviolet (UV) radiation. Although darker skin tones contain more melanin, which offers some natural protection against UV rays, it isn't enough to prevent all damage.
Sunburn occurs when the skin is exposed to excessive UV radiation, leading to redness, pain, and peeling. People with dark skin may have a higher natural sun protection factor (SPF) due to the higher melanin content, but this doesn't make them invincible. Darker skin can still burn, especially in areas that aren't commonly exposed to the sun, such as the back, chest, and scalp.
Additionally, sun damage can occur even without visible signs of sunburn. UV radiation can penetrate the skin, causing long-term damage and increasing the risk of skin cancer. Dark skin may have a lower risk of developing skin cancer compared to lighter skin tones, but it isn't completely exempt.
To prevent sunburn and sun damage, it's crucial for individuals with dark skin to use sun protection measures such as wearing protective clothing, seeking shade when the sun is strongest, and applying sunscreen. Although sunscreen is often associated with lighter skin tones, it's equally important for people with dark skin. While the higher melanin content offers some protection, it isn't sufficient to provide full protection against UV radiation. Choosing a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an adequate SPF and regularly reapplying it can help reduce the risk of sunburn and long-term sun damage.
Importance of Preventing Hyperpigmentation
To effectively protect your dark skin from the harmful effects of the sun, it's crucial to understand the importance of preventing hyperpigmentation. Hyperpigmentation refers to the darkening of certain areas of the skin caused by an overproduction of melanin, the pigment that gives color to our skin. This condition can be triggered by excessive sun exposure, and it's more common in individuals with darker skin tones.
To prevent discoloration and maintain an even skin tone, here are four key reasons why you should prioritize sun protection:
- UV radiation: The sun emits ultraviolet (UV) radiation, which can penetrate the skin and stimulate the production of melanin. Darker skin already contains more melanin, making it more susceptible to hyperpigmentation when exposed to UV rays.
- Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation: Dark spots or patches of hyperpigmentation can develop after skin inflammation or injury, such as acne or cuts. Sun exposure can worsen these marks and make them even more noticeable.
- Uneven distribution of melanin: Darker skin contains melanin in a more dispersed manner, making it prone to uneven pigmentation. Without proper sun protection, areas of the skin that are already hyperpigmented may become even darker.
- Preventive measures: Using broad-spectrum sunscreen, wearing protective clothing, and seeking shade can help prevent hyperpigmentation. These measures minimize the impact of UV radiation on your skin, reducing the risk of discoloration and promoting an even skin tone.
Skin Cancer Risks for Darker Skin Tones
Protecting your dark skin from the sun is crucial, as it can help reduce the risk of skin cancer. While it's true that individuals with darker skin tones have a higher natural protection against harmful UV radiation compared to those with lighter skin, it doesn't mean they're immune to the dangers of the sun. Skin cancer can still occur in individuals with dark skin, although it may be less common.
Skin cancer prevention is essential for everyone, regardless of skin tone. UV radiation from the sun can damage the DNA in skin cells, leading to mutations and the development of cancer cells. Although dark skin has more melanin, which provides some natural protection against UV radiation, it isn't foolproof. UV radiation can still penetrate the skin, causing cellular damage and increasing the risk of skin cancer.
It is important for individuals with dark skin to practice sun protection measures to minimize their risk. This includes seeking shade during peak sun hours, wearing protective clothing such as wide-brimmed hats and long-sleeved shirts, and using broad-spectrum sunscreen with a high SPF. Regular self-examinations of the skin are also crucial to detect any suspicious moles or growths early on. Consulting with a dermatologist regularly is recommended to monitor the health of your skin and to address any concerns or changes.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Dark-Skinned Individuals Still Get Sunburned?
Yes, dark-skinned individuals can still get sunburned. Sunburn occurs when the skin is damaged by the sun's UV rays. Therefore, people with dark skin need to wear sunscreen to protect themselves from sunburn and other harmful effects of the sun.
Is It True That People With Dark Skin Don't Need to Wear Sunscreen?
You might have heard the myth that people with dark skin don't need sunscreen, but that's not true. There are misconceptions about sunscreen for dark skin, and it's important for everyone to protect themselves from the harmful effects of the sun.
Are There Any Specific Products or Ingredients That Are Recommended for Sun Protection on Dark Skin?
Recommended products and alternative remedies can provide adequate sun protection for dark skin. It is important to choose sunscreen with broad-spectrum protection and an SPF of at least 30. Additionally, clothing, hats, and sunglasses can further shield your skin from harmful UV rays.
Can Hyperpigmentation Be Reversed or Treated?
Hyperpigmentation treatments can help reverse or treat hyperpigmentation. There are various options available, including topical creams, chemical peels, laser therapy, and microdermabrasion. Natural remedies for hyperpigmentation, like lemon juice or aloe vera, may also be effective.
What Are the Most Common Types of Skin Cancer That Affect People With Darker Skin Tones?
The most common types of skin cancer that affect people with darker skin tones are basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma. It's important to debunk common misconceptions and emphasize the importance of regular skin checks for everyone.
Conclusion
In conclusion, sun protection is crucial for individuals with dark skin due to their higher risk of skin damage, misconceptions about sun protection, and the possibility of sunburn and sun damage.
Additionally, preventing hyperpigmentation and minimizing the risk of skin cancer are significant reasons to prioritize sun protection.
Remember, just because dark skin offers some natural protection against the sun's harmful rays doesn't mean it's immune. After all, an ounce of prevention is worth a pound of cure.
Stay sun-safe!