'Helping Children Overcome PTSD: A Step-by-Step Guide' is a comprehensive resource designed to assist professionals, parents, and caregivers in supporting children who have experienced trauma.
This guide offers practical strategies and evidence-based techniques to help children heal from the effects of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
With a focus on understanding childhood PTSD, recognizing signs and symptoms, and seeking appropriate professional help, this guide provides a step-by-step approach to addressing and managing the challenges faced by children with PTSD.
By implementing trauma-informed care and fostering a supportive environment, caregivers can play a crucial role in facilitating the healing process for these vulnerable individuals.
This guide is a valuable tool for anyone involved in the care and support of children affected by PTSD.
Understanding Childhood PTSD
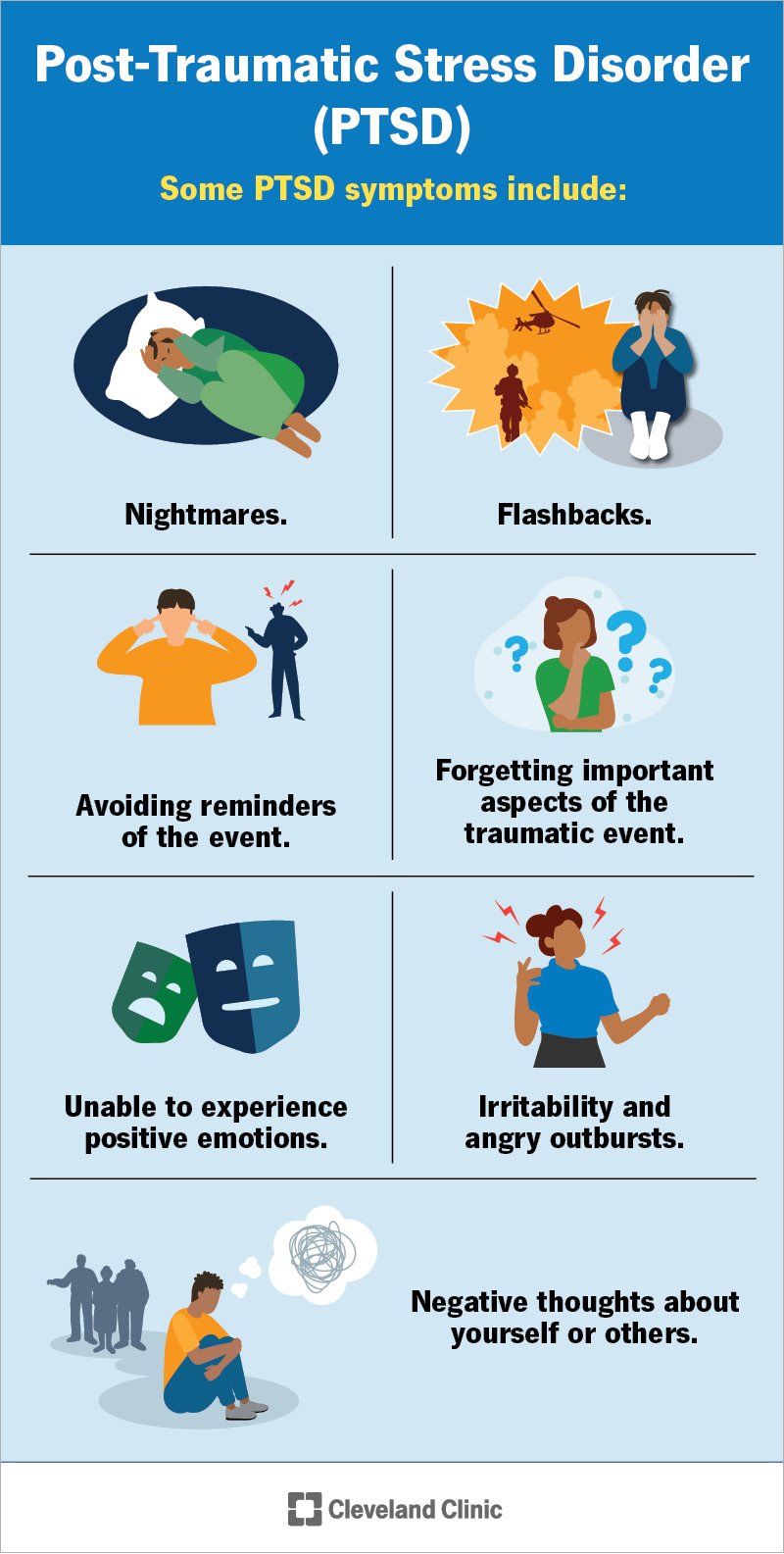
Understanding Childhood PTSD is essential for anyone working with children who have experienced trauma. Childhood PTSD, or Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder, is a mental health condition that can develop in children who have experienced or witnessed a traumatic event. It is crucial to have a deep understanding of this condition in order to provide appropriate support and care to these children.
Children with PTSD may exhibit a range of symptoms, including re-experiencing the traumatic event through nightmares or flashbacks, avoiding reminders of the trauma, experiencing negative changes in mood and cognition, and displaying heightened anxiety and arousal. These symptoms can significantly impact a child's daily functioning, relationships, and overall well-being.
Empathy and sensitivity are key when working with children who have experienced trauma. It is vital to create a safe and supportive environment where children feel comfortable expressing their thoughts and emotions. Building trust and establishing a strong therapeutic alliance is essential for effective treatment.
Educating oneself about childhood PTSD can help professionals better understand the unique needs and challenges faced by these children. This knowledge can guide the development of individualized treatment plans that address the specific symptoms and difficulties experienced by each child. By providing appropriate support and intervention, professionals can help children overcome the effects of trauma and lead fulfilling lives.
Recognizing Signs and Symptoms
To effectively address childhood PTSD, professionals must be able to accurately recognize the signs and symptoms exhibited by children who have experienced trauma. It is crucial to pay close attention to the indicators displayed by these children, as early identification and intervention can greatly improve their chances of recovery.
Children who have experienced trauma may exhibit a range of signs and symptoms that can manifest in various ways. One common symptom is re-experiencing the traumatic event through nightmares or flashbacks. These intrusive thoughts can be distressing and cause the child to feel overwhelmed. Another sign is avoidance, where the child actively avoids reminders or situations that trigger memories of the trauma. They may withdraw from social activities, isolate themselves, or refuse to discuss the event.
Emotional and behavioral changes are also key indicators of childhood PTSD. Children may become irritable, easily startled, or have difficulty concentrating. They may experience heightened anxiety, exhibit aggressive behavior, or struggle with sleep disturbances. Additionally, regression in their development, such as bedwetting or clinginess, may occur.
Recognizing these signs and symptoms is essential in providing the necessary support and intervention for children with PTSD. By understanding these indicators, professionals can work towards helping children overcome their trauma and facilitating their journey towards healing and resilience.
Seeking Professional Help
Professional intervention is crucial for children with PTSD to receive the necessary support and guidance in their journey towards healing and recovery. Seeking professional help can make a significant difference in a child's ability to cope with and overcome the effects of trauma.
Here are five important steps to consider when seeking professional help for a child with PTSD:
- Research and choose a qualified therapist: Look for a therapist who specializes in treating children with PTSD. Consider their experience, credentials, and approach to therapy to ensure a good fit for your child's needs.
- Collaborate with the therapist: Establish open lines of communication with the therapist and actively participate in your child's treatment. Share any relevant information and work together to develop a personalized treatment plan.
- Explore evidence-based therapies: Seek out therapies that have been proven effective in treating PTSD in children, such as Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) or Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR). These therapies can help your child process and manage their traumatic experiences.
- Encourage a safe and supportive environment: Create a nurturing and understanding environment at home, where your child feels safe to express their feelings and experiences. This supportive atmosphere can complement the therapeutic work and enhance your child's healing process.
- Access support for yourself: Taking care of a child with PTSD can be emotionally challenging. Seek support for yourself from friends, family, or support groups. Caring for your own well-being will allow you to better support your child through their recovery.
Implementing Trauma-Informed Care
When implementing trauma-informed care for children with PTSD, it is essential to create an environment that prioritizes their emotional well-being and fosters a sense of safety and understanding. Trauma-informed care is an approach that recognizes the impact of trauma on a child's development and behavior, and aims to provide support and healing in a sensitive and empathetic manner.
One effective way to implement trauma-informed care is by creating a trauma-informed classroom or therapeutic setting. This can be achieved by incorporating the following key elements:
| Key Elements of Trauma-Informed Care | Examples of Implementation |
|---|---|
| Safety | Creating a calm and predictable environment. Implementing clear rules and boundaries. |
| Trust | Building trusting relationships with the child through consistent and reliable support. |
| Choice | Offering choices and empowering the child to make decisions within appropriate limits. |
| Collaboration | Collaborating with the child, their family, and other professionals to develop a comprehensive treatment plan. |
| Empowerment | Encouraging the child to express their thoughts and feelings through art, play, or other creative outlets. |
Supporting the Healing Process
Supporting the child's healing process is a crucial aspect of implementing trauma-informed care for children with PTSD. To effectively support their healing journey, it is important to provide them with the necessary tools and resources. Here are five key ways to support the healing process:
- Create a safe and supportive environment: Establishing a safe and supportive environment is essential for children with PTSD. This can be achieved by ensuring a calm and predictable atmosphere, where the child feels secure and understood.
- Encourage open communication: Encouraging the child to express their thoughts and feelings can be instrumental in their healing process. Active listening, validation, and empathy are vital components of effective communication.
- Provide therapeutic interventions: Engaging the child in evidence-based therapeutic interventions, such as trauma-focused cognitive-behavioral therapy, can help them process their traumatic experiences and develop healthy coping strategies.
- Promote self-care practices: Teaching the child self-care practices, such as relaxation techniques, mindfulness exercises, and healthy lifestyle habits, can empower them to take an active role in their healing process.
- Collaborate with caregivers and professionals: Building a strong support network is crucial. Collaborating with caregivers, teachers, and mental health professionals can ensure that the child receives consistent and comprehensive care.
By implementing these strategies and providing ongoing support, we can facilitate the child's healing process and help them overcome the challenges associated with PTSD.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Can I Determine if My Child's Symptoms Are Due to PTSD or Another Mental Health Condition?
To determine if your child's symptoms are due to PTSD or another mental health condition, it is essential to consult with a qualified mental health professional who can conduct a thorough evaluation and provide an accurate diagnosis.
What Are Some Common Misconceptions About Childhood PTSD That I Should Be Aware Of?
Some common misconceptions about childhood PTSD include the belief that children are resilient and will simply outgrow their symptoms, or that they are too young to experience trauma. It is important to be aware of these misconceptions in order to provide appropriate support and intervention.
Are There Any Alternative Therapies or Treatments That Can Be Used Alongside Traditional Methods to Help Children Overcome Ptsd?
Alternative therapies or treatments can be used alongside traditional methods to help children overcome PTSD. These may include art therapy, play therapy, yoga, and mindfulness exercises, which can provide additional support and promote healing.
Can Trauma-Informed Care Be Implemented at Home and in School Settings, or Is It Primarily for Professional Use?
Trauma-informed care can be implemented both at home and in school settings, promoting a supportive environment for children affected by PTSD. While primarily used by professionals, caregivers and educators can adopt its principles to create a conducive space for healing and recovery.
How Long Does the Healing Process Typically Take for Children With PTSD, and Are There Any Factors That Can Speed up or Slow Down the Recovery?
The healing process for children with PTSD varies depending on individual factors such as the severity of the trauma and the support system in place. Factors that can speed up recovery include early intervention, a stable and nurturing environment, and access to effective therapeutic interventions. Conversely, factors that can slow down recovery include ongoing exposure to trauma, lack of support, and limited access to mental health resources.